Advantages of Coatings on Cutter Blades
The use of coatings on cutter blades for industrial cutting and machining, has numerous advantages for performance and longevity, including the reduction of downtime. In this article we will look in depth at a number of the most popular coatings and compare them for relative advantages, performance and durability.
The Tin Coating Advantage
In the world of industrial cutting and machining, the performance and longevity of the cutting tools are paramount. One crucial aspect that can significantly impact the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these tools is the use of coatings on the blades. Among the various coating options available, tin (Sn) coatings have emerged as a popular choice, particularly for tungsten carbide blades used in plotter and cutter machines.
At X-Keenblades, we have extensive experience with tin coatings on tungsten carbide blades. Typically, we apply a coating thickness of around 2 microns (μ) to these blades. While the added thickness may slightly compromise the initial sharpness of the blade, this effect is often short-lived. As the blade is used, the tin layer gradually wears down, resulting in a sharper cutting edge and a corresponding reduction in the cutting force required.
When utilizing tin-coated tungsten carbide blades in plotter and cutter machines, we have observed a significant increase in their lifespan, with a minimum extension of 30% (up to 10 x) compared to non-coated blades. This extended lifespan translates to substantial cost savings, as the average price of a tungsten carbide blade is typically increased by only around 10% (ballpark figure tin coating vs tungsten carbide plotter blade) due to the tin coating process.
The real advantage, however, lies in the reduced machine downtime. By extending the lifespan of the cutting blades, operators can enjoy more consistent and reliable performance, minimizing the need for frequent blade replacements and the associated disruptions to production.
Hybrid and Multilayer Coatings
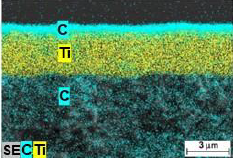
DLC-topcoating op een Tin-coatlaag. De totale dikte varieert tussen 2.59 en 2,95 µm.
While tin coatings have proven to be a reliable and cost-effective solution, the world of cutting tool coatings continues to evolve. One emerging trend is the use of hybrid or multilayer coatings, which combine the benefits of various coating materials and techniques.
Hybrid or multilayer coatings are used in a wide range of applications where good adhesion of the coating to the base material is crucial, as well as for the application of hard and slippery coatings that reduce friction and do not require perfect cooling. These advanced coating systems can provide enhanced performance characteristics, such as improved wear resistance, reduced friction, and enhanced corrosion protection.
Coating Thickness and Sharpness
As mentioned earlier, the added thickness of the tin coating can slightly compromise the initial sharpness of the blade. This is a trade-off that must be considered when selecting the appropriate coating thickness. A thicker coating may offer increased wear resistance and longevity, but it may also result in a less sharp cutting edge, especially during the initial use of the blade.
To address this challenge, manufacturers and end-users often experiment with different coating thicknesses to find the optimal balance between sharpness, wear resistance, and overall performance. In some cases, a thinner coating may be preferred to maintain a sharper cutting edge, while in other applications, a thicker coating may be more suitable to maximize the blade’s lifespan.
Coating Adhesion and Durability
Another critical factor in the success of coatings on cutting blades is the adhesion and durability of the coating itself. A poorly adhered or easily-worn coating can quickly negate the benefits of the coating, leading to premature failure and the need for more frequent blade replacements.
Manufacturers of coated cutting blades invest significant resources into developing and refining their coating processes to ensure superior adhesion and durability. This may involve the use of specialized surface preparation techniques, the optimization of coating parameters, and the incorporation of adhesion-promoting layers or graded compositions within the coating structure.
Customization and Application-Specific Coatings
As the demands on cutting tools continue to evolve, the need for customized and application-specific coatings has become increasingly important. Different industries and applications may require unique coating characteristics, such as enhanced corrosion resistance, improved lubricity, or the ability to withstand specific operating environments.
Manufacturers of coated cutting blades often work closely with their customers to understand the specific requirements of their applications and develop tailored coating solutions to meet those needs. This level of customization can help ensure that the cutting blades perform optimally in their intended use, maximizing efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
The use of coatings on cutting blades, particularly tin coatings on tungsten carbide blades, can provide significant advantages in terms of extended lifespan, reduced machine downtime, and improved cost-effectiveness. As the industry continues to evolve, the development of hybrid and multilayer coatings, as well as the customization of coating solutions to specific applications, will play an increasingly important role in optimizing the performance of cutting tools.
By understanding the benefits and considerations of coatings on cutting blades, buyers, engineers, and production managers can make informed decisions that contribute to the overall efficiency and profitability of their manufacturing operations.





